GenAI Roadmap: A Guide for Enterprises on How to Implement Gen AI Applications
- Chatzy.ai
- Jun 25, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Jul 18, 2024
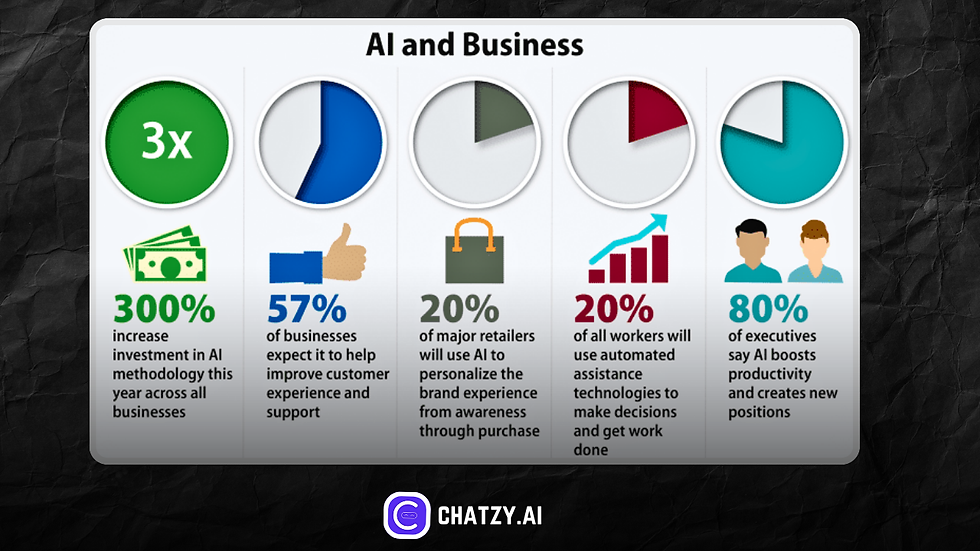
In an era of rapid technological advancements, generative artificial intelligence stands out as a transformative force that has already reshaped industries and sparked innovation.
Whether you’re a seasoned AI enthusiast or a business owner eager to harness the power of creative machines, our comprehensive guide given below is your gateway to understanding and implementing generative AI in an enterprise environment.
Design an adaptable system architecture
Companies will need to develop a net-new, end-to-end architecture and strategy to support the use of generative AI. This includes identifying all critical program components, such as integrations, data sourcing practices, and maintenance.
Companies need a flexible framework that can change with the business’s needs, goals, and capabilities, as well as adapt to market and regulatory forces.
Ethical considerations
Generative AI raises many unique security and compliance issues. Companies will need to develop policies and procedures to establish program guardrails.
They can also lower risk by initially focusing on internal applications that can be closely monitored and controlled. They need to develop policies and procedures for the conduct.
Create new KPIs to measure impact
The goal of a new technology introduction like generative AI is not necessarily to deliver an ROI in the initial phase. Instead, the goal is to prove the technology works in the environment and has the potential to deliver value and impact.
New KPIs are needed that are specific to the identified use case. It’s important to go beyond traditional metrics to determine the business impact of the program and get a more complete sense of how to adapt in the future.
Invest in external expertise
Out of the eight billion people on the planet, less than 200,000 know how to operate an AI system. This begs the question: Does your company have the internal expertise to move the program forward?
Most organizations will need to tap a transformation or technology partner to help evaluate platforms, introduce it to the organization and identify the other technology elements needed to integrate it across the enterprise. Hence investing in technical expertise is a must step to take for enterprises.
Input Validation and Sanitization
One of the primary security measures is to validate and sanitize user inputs. This process helps prevent common vulnerabilities such as injection attacks, where an attacker can input malicious data to manipulate the system. It’s imperative to scrutinize every input, ensuring that it cannot interfere with the backend processes.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Compliance with data protection regulations is not optional; it’s mandatory. Implementing measures to safeguard user privacy, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits are necessary. By adhering to these principles, developers can build trust with users and ensure that their applications are both secure and compliant.
Model Robustness and Domain Fit
Key aspect of model robustness is its ability to withstand and counter adversarial attacks.
Strengthening an LLM involves training it with a diverse set of scenarios, and employing techniques such as adversarial training and input filtering. This not only improves its resistance to manipulation but also enhances the model’s overall performance and reliability.
Here are some of the main challenges in implementing generative AI
1) Data Quality and Quantity
Generative AI models require massive amounts of high-quality training data to function accurately and generate relevant outputs. Many organizations struggle to obtain sufficient domain-specific data that represents their products or services.
2) Biases and Ethical Concerns
There are risks of generative AI models producing biased, discriminatory, or offensive content if trained on biased datasets or without proper safeguards. Ensuring the ethical and responsible use of AI is crucial to maintain trust.
3) Intellectual Property Issues
Training data may contain copyrighted or proprietary information, raising legal concerns over ownership and usage rights of the AI-generated content.
4) Lack of Transparency and Explainability
The decision-making processes of deep learning models are often opaque “black boxes”, lacking transparency and making it difficult to explain their outputs. This lack of explainability hinders trust and adoption.
Frequently asked questions:
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence technology capable of creating new and realistic content in response to prompts. It can generate various types of content such as text, audio, images, videos, software code, product designs, and synthetic data.
Why is Generative AI essential for businesses?
Generative AI offers benefits such as enhanced creativity, better decision-making, improved customer service, increased efficiency, and scalability. It can automate tasks, personalize customer experiences leading to operational efficiency and competitive advantages.
What skills do employees need to adapt to a GenAI-powered workplace?
Data Literacy: Develop a strong understanding of data-related concepts like data collection, cleaning, and analysis.
Critical Thinking: Enhance the ability to evaluate GenAI outputs, identify biases, and flag potential ethical concerns.
Technical Understanding: Build a basic technical understanding of how GenAI models work, even without becoming a data scientist.
Adaptability: Embrace continuous learning and a willingness to adapt to new technologies and workflows.
Collaboration: Foster teamwork between human experts and AI systems to optimize processes and outcomes.



